Chapter 22--Fourier Series: Fundamental Period, Frequency, and Angular Frequency: Difference between revisions
Andrew.roth (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Andrew.roth (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
==Reviewers== |
==Reviewers== |
||
Brandon Vazquez |
Brandon Vazquez |
||
Ben Blackley |
|||
==Readers== |
==Readers== |
||
Thomas Wooley |
Thomas Wooley |
||
Revision as of 10:49, 11 January 2010
22 lines (currently)
1 reference
1 figure
123 points
Period, Frequency, and Angular Frequency
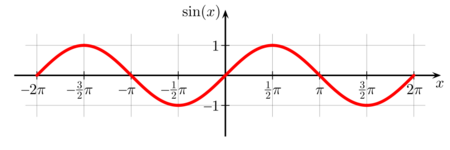
Period
Long long ago, in a high school class called trigonometry, we leaned about periodic functions. A periodic function is a function that repeats itself over and over for infinity. The period of the function is the distance of one iteration that is infinitely repeating.
Where T is the period
The picture to the right shows the plot of the standard sine function whose period is . What the plot does not show is that the line keeps extending and repeating the bumps and valleys over the whole x axis, or . But wait! Can't the period also be or ? In fact it can. Because the graph of sin(x) repeats itself every units, the period of the function is actually where n is any whole number from zero to Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \infty}
Frequency and Angular Frequency
The Frequency is the number of periods per second and is defined mathematically as
The standard unit of measurement for frequency is Hz (Hertz). 1 Hz = 1 cycle/second
The Angular Frequency is defined as
The standard unit of measurement for angular frequency is in radians/second.
Fundamental Period, Frequency, and Angular Frequency
The fundamental period is the smallest positive real number for which the periodic equation holds true.
The fundamental frequency is defined as .
The fundamental angular frequency is defined as .
References
<references />
Author
Andrew Roth
Reviewers
Brandon Vazquez Ben Blackley
Readers
Thomas Wooley












