Example Problems with Transformers: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
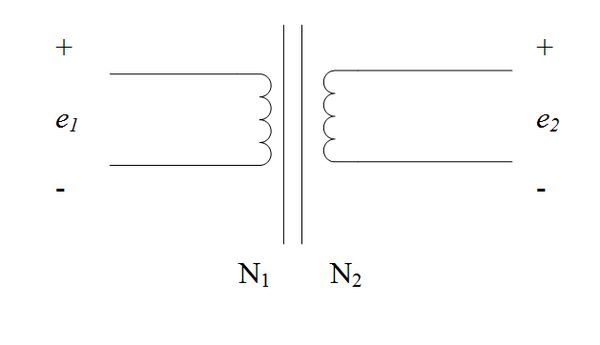
'''Problem 1.''' An ''ideal'' step down transformer has a winding of <math> N_1 = 10 \text{ turns and } N_2 = 2 </math> turns. If the input voltage is 1200V, what is the resulting output voltage? |
'''Problem 1.''' An ''ideal'' step down transformer has a winding of <math> N_1 = 10 \text{ turns and } N_2 = 2 </math> turns. If the input voltage is 1200V, what is the resulting output voltage? |
||
'''Solution''' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
By modifying equation 5-39 (Mohan 5-22) we can obtain an equation for the output voltage. That is, |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<br/> |
|||
<div style="text-align:center"> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
</div> |
|||
<br/> |
|||
With the information above we can now determine the output voltage: |
|||
<br/> |
|||
<div style="text-align:center"> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
</div> |
|||
<center> |
<center> |
||
Revision as of 17:34, 26 January 2010
Problems 1-3
Kevin Starkey, Nick Christman, Aric Vyhmeister
Problem 1. An ideal step down transformer has a winding of turns. If the input voltage is 1200V, what is the resulting output voltage?
Solution
By modifying equation 5-39 (Mohan 5-22) we can obtain an equation for the output voltage. That is,
.
With the information above we can now determine the output voltage: