Fourier Series: Explained!: Difference between revisions
Michaelvier (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==A Brief Introduction== |
==A Brief Introduction== |
||
A Fourier series is a mathematical tool that takes a periodic function and turns it into a sum of simple oscillating functions (i.e. sines and cosines)<ref> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_series Fourier Series] |
A Fourier series is a mathematical tool that takes a periodic function and turns it into a sum of simple oscillating functions (i.e. sines and cosines)<ref> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_series Fourier Series]</ref>. These series were discovered by Joseph Fourier to solve a heat equation in a metal plate. |
||
==How They Work== |
==How They Work== |
||
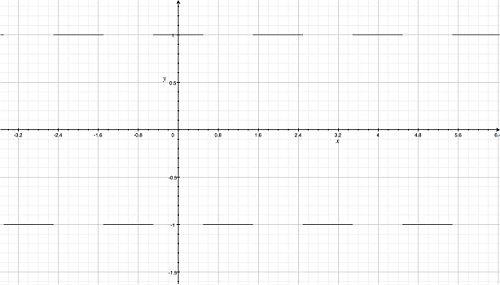
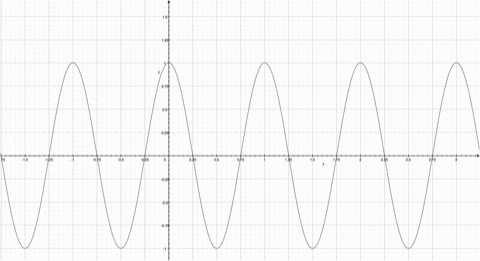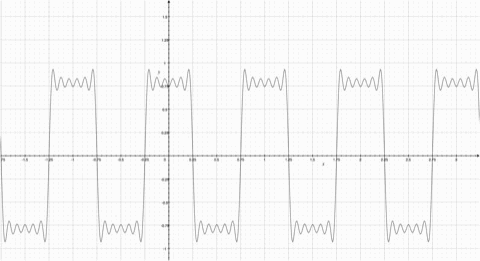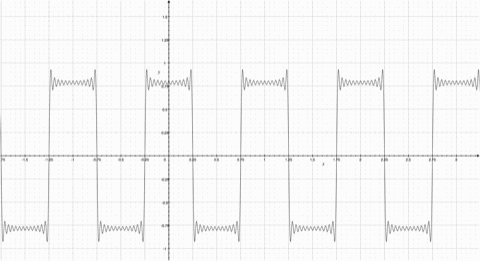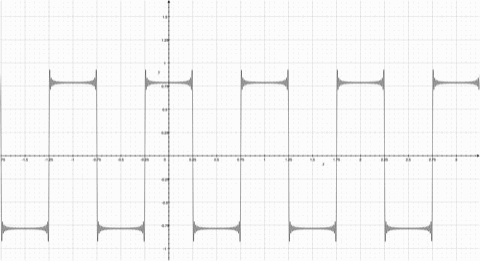
Fourier Series represents a periodic function through a sum of sines or cosines. Each term in the summation has a frequency n. The first term has the same frequency as the periodic function, the second term has twice the frequency of the periodic function, and so on. The more functions added, the more the summation resembles the step function. Observe the animation; notice how the summation function resembles the original periodic function more as more functions are added. |
Fourier Series represents a periodic function through a sum of sines or cosines. Each term in the summation has a frequency n. The first term has the same frequency as the periodic function, the second term has twice the frequency of the periodic function, and so on. The more functions added, the more the summation resembles the step function. Observe the animation; notice how the summation function resembles the original periodic function more as more functions are added. |
||
Revision as of 23:35, 11 January 2010
A Brief Introduction
A Fourier series is a mathematical tool that takes a periodic function and turns it into a sum of simple oscillating functions (i.e. sines and cosines)<ref> Fourier Series</ref>. These series were discovered by Joseph Fourier to solve a heat equation in a metal plate.
How They Work
Fourier Series represents a periodic function through a sum of sines or cosines. Each term in the summation has a frequency n. The first term has the same frequency as the periodic function, the second term has twice the frequency of the periodic function, and so on. The more functions added, the more the summation resembles the step function. Observe the animation; notice how the summation function resembles the original periodic function more as more functions are added.
References
<references/>