Class Notes 1-5-2010: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Brian.Roath (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
:<math> \vec{v} \cdot \mathbf{\hat{i}} = v_\mathrm{x} </math> |
:<math> \vec{v} \cdot \mathbf{\hat{i}} = v_\mathrm{x} </math> |
||
:<math> \vec{v} \cdot \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{m} = \sum_{i} v_\mathrm{i} \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{i} \cdot \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{m} = v_\mathrm{m} </math> |
:<math> \vec{v} \cdot \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{m} = \sum_{i} v_\mathrm{i} \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{i} \cdot \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{m} = v_\mathrm{m} </math> |
||
:<math> \delta_\mathrm{i,m} \equiv \begin{cases} 1 & \mbox{if } i = m |
:<math> \delta_\mathrm{i,m} \equiv \begin{cases} 1, & \mbox{if } i = m \\ 0, & \mbox{else} \end{cases}</math> |
||
==Example== |
==Example== |
||
Revision as of 16:23, 17 January 2010
This article covers the notes given in class on January 5, 2010.
Subjects Covered
1) Linear Systems
2) Functions as Vectors
- Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{v} = \sum_{i} v_\mathrm{i} \mathbf{\hat{a}}_\mathrm{i} }
Example
Given function:
1) Use vector analogy
External Links
Authors
Colby Fullerton
Brian Roath










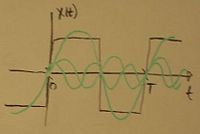

![{\displaystyle x(t)=\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\left[b_{n}\sin \left(\left({\frac {2\pi n}{T}}\right)t\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1b15fa18143738e6bbe3d2aefb2cc8a5ac979bb7)
![{\displaystyle x(t)\cdot \sin \left({\frac {2\pi mt}{T}}\right)=\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\left[b_{n}\sin \left(\left({\frac {2\pi n}{T}}\right)t\right)\cdot \sin \left({\frac {2\pi mt}{T}}\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/570a428f69ebcdd14e9a313bceea1472ddbf5f67)
