|
|
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 113: |
Line 113: |
|
</math> |
|
</math> |
|
== Eigen Values == |
|
== Eigen Values == |
|
Once you have your equations of equilibrium in matrix form you can plug them into a calculator or a computer program that will give you the eigen values automatically. This saves you a lot of hand work. Here's what you should come up with for this particular problem given these initial conditions. |
|
'''Once you have your equations of equilibrium in matrix form you can plug them into MATLAB which will give you the eigen values automatically.''' |
|
:'''Given''' |
|
:'''Given''' |
|
:<math>m_1=10kg\,</math> |
|
:<math>m_1=10kg\,</math> |
| Line 120: |
Line 120: |
|
:<math>k_2=50\,{N\over {m}}</math> |
|
:<math>k_2=50\,{N\over {m}}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
We now have |
|
'''We now have''' |
|
:<math>\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>\begin{bmatrix} |
|
\dot{x_1} \\ |
|
\dot{x_1} \\ |
| Line 149: |
Line 149: |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
From this we get |
|
'''From this we get''' |
|
:<math>\lambda_1=\,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_1=-3.0937,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_2=\,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_2=2.1380i,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_3=\,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_3=- 2.1380i,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_4=\,</math> |
|
:<math>\lambda_4=3.0937,</math> |
|
|
|
|
== Eigen Vectors == |
|
== Eigen Vectors == |
|
Using the equation above and the same given conditions we can plug everything to a calculator or computer program like MATLAB and get the eigen vectors which we will denote as <math>k_1,k_2,k_3,k_4\,</math>. |
|
'''Using the equation above and the same given conditions we can plug everything into MATLAB and get the eigen vectors which we will denote as <math>k_1,k_2,k_3,k_4\,</math>.''' |
|
:<math>k_1=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>k_1=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
0 \\ |
|
0.0520 \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
-0.1609 \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
-0.3031 \\ |
|
|
0.9378 |
|
0 |
|
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
:<math>k_2=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>k_2=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
0 \\ |
|
0.4176i \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
-0.8928 \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
- 0.0716i \\ |
|
|
0.1532 |
|
0 |
|
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
:<math>k_3=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>k_3=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
0 \\ |
|
- 0.4176i \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
-0.8928 \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
0.0716i \\ |
|
|
0.1532 |
|
0 |
|
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
:<math>k_4=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>k_4=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
0 \\ |
|
-0.0520 \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
-0.1609 \\ |
|
0 \\ |
|
0.3031 \\ |
|
|
0.9378 |
|
0 |
|
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
| ⚫ |
|
|
| ⚫ |
In this section we will use matrix exponentials to solve the same problem. First we start with this identity. |
|
| ⚫ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
==So then the answer is...== |
|
This can be rearranged by multiplying the inverse of T to the left side of the equation. |
|
|
|
'''We can now plug these eigen vectors and eigen values into the standard equation''' |
| ⚫ |
:<math> T^{-1}z =x\,</math> |
|
|
|
:<math>x=c_1k_1e^{\lambda_1 t}+c_2k_2e^{\lambda_2 t}+c_3k_3e^{\lambda_3 t}+c_4k_4e^{\lambda_4 t}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
<math>\ x=c_1</math><math>\begin{bmatrix}0.0520 \\-0.1609 \\-0.3031\\0.9378\end{bmatrix}\,</math><math>e^{-3.0937}+ c_2</math><math>\begin{bmatrix}0.4176i \\-0.8928\\- 0.0716i\\0.1532\end{bmatrix}\,</math><math>e^{2.1380i}+ c_3</math><math>\begin{bmatrix}- 0.4176i \\-0.8928\\0.0716i\\0.1532\end{bmatrix}\,</math><math>e^{- 2.1380i}+ c_4</math><math>\begin{bmatrix}-0.0520 \\-0.1609\\0.3031\\0.9378\end{bmatrix}\, |
|
Now we can use another identity that we already know |
|
|
:<math>\dot{x}=Ax</math>
|
|
</math><math>e^{3.0937}\,</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
⚫ |
|
|
Combining the two equations we then get |
|
|
⚫ |
'''We now use matrix exponentials to solve the same problem. ''' |
|
:<math>T^{-1}\dot{z}=AT^{-1}z</math> |
|
|
⚫ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multiplying both sides of the equation on the left by T we get
|
|
'''So from the above equation we get this to prove the matrix exponetial works.''' |
|
:<math>\dot{z}=TAT^{-1}z</math> |
|
:<math>\dot{z}=TAT^{-1}z</math> |
|
|
|
|
| Line 202: |
Line 202: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
We also know what T equals and we can solve it for our case |
|
'''We also know what T equals and we can solve it for our case''' |
|
:<math>T^{-1}=[k_1|k_2|k_3|k_4]\,</math> |
|
:<math>T^{-1}=[k_1|k_2|k_3|k_4]\,</math> |
|
:<math>T^{-1}=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>T^{-1}=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ |
|
0.0520 & 0.4176i & - 0.4176i & -0.0520 \\ |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ |
|
-0.1609 & -0.8928 & -0.8928 & -0.1609 \\ |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ |
|
-0.3031 & - 0.0716i & 0.0716i & 0.3031 \\ |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 |
|
0.9378 & 0.1532 & 0.1532 & 0.9378 |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
Taking the inverse of this we can solve for T |
|
'''Taking the inverse of this we can solve for T''' |
|
:<math>T=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
:<math>T=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ |
|
-0.2914 & 0.0943 & -1.6996 & 0.5493 \\ |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
|
|
- 1.2337i & -0.5770 & - 0.2117i & -0.0990 \\ |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
|
|
1.2335i & -0.5770 & 0.2116i & -0.0990 \\ |
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 |
|
0.2914 & 0.0943 & 1.6996 & 0.5493 |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
'''So taking''' |
|
⚫ |
:<math> \dot{z}=TAT^{-1}z</math> |
|
|
'''We get the uncoupled matrix of''' |
|
|
:<math>\dot{z}=\begin{bmatrix} |
|
|
-3.0937 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ |
|
|
0 & 2.1380i & 0 & 0 \\ |
|
|
0 & 0 & - 2.1380i & 0 \\ |
|
|
0 & 0 & 0 & 3.0937 |
|
|
\end{bmatrix}</math> |
|
|
|
|
|
created by Greg Peterson |
Problem Statement
Write up on the Wiki a solution of a coupled oscillator problem like the coupled pendulum. Use State Space methods. Describe the eigenmodes and eigenvectors of the system.
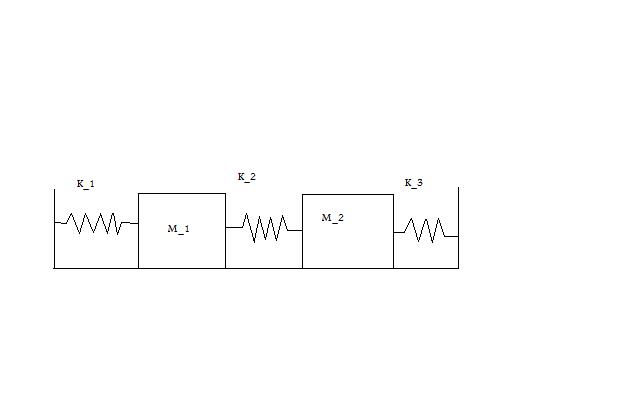
Initial Conditions:





Equations for M_1

Equations for M_2

Additional Equations


State Equations
 =
=

With the numbers...
 =
=

Eigen Values
Once you have your equations of equilibrium in matrix form you can plug them into MATLAB which will give you the eigen values automatically.
- Given




We now have

From this we get




Eigen Vectors
Using the equation above and the same given conditions we can plug everything into MATLAB and get the eigen vectors which we will denote as  .
.




So then the answer is...
We can now plug these eigen vectors and eigen values into the standard equation










Matrix Exponential
We now use matrix exponentials to solve the same problem.

So from the above equation we get this to prove the matrix exponetial works.

We also know what T equals and we can solve it for our case
![{\displaystyle T^{-1}=[k_{1}|k_{2}|k_{3}|k_{4}]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b489191884d4a54127086ec332d536997cb30434)

Taking the inverse of this we can solve for T

So taking

We get the uncoupled matrix of

created by Greg Peterson





































![{\displaystyle T^{-1}=[k_{1}|k_{2}|k_{3}|k_{4}]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b489191884d4a54127086ec332d536997cb30434)


