EMEC - Greg: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(New page: =Definitions= {|border="1" | Symbol || Units || Name |- | <math>\overrightarrow{E}</math>|| <math>\frac{V}{M}</math> || Electric Field Intensity |- | <math>\overrightarrow{D}</math>|| <ma...) |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Definitions= |
===Definitions=== |
||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnetism#Units Electromagnetism Units] |
|||
{|border="1" |
{| class="wikitable" border="1" |
||
! Symbol !! Units !! Name !! Definition |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|||
| <math>\overrightarrow{E}</math>|| <math>\frac{V}{M}</math> || Electric Field Intensity |
|||
| |
|||
| Flux |
|||
| A scalar value. The rate of transfer of energy (or another physical quantity) per unit area. <ref> [http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/flux#Noun Wiktionary - Flux] </ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| <math>\overrightarrow{ |
| <math>\overrightarrow{E}</math> |
||
| <math>\frac{V}{M}</math> |
|||
| Electric field (intensity/strength) |
|||
| The space surrounding an electric charge. It will exert a force on other electrically charged objects. |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| <math>\overrightarrow{ |
| <math>\overrightarrow{D}</math> |
||
| <math>\frac{C}{M^2}</math> |
|||
| Electric (flux density/displacement field) |
|||
| The amount of electric flux in a unit area perpendicular to the direction of electric field |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| <math>\overrightarrow{ |
| <math>\overrightarrow{H}</math> |
||
| <math>\frac{A}{M}</math> |
|||
| Magnetic field (intensity/strength) |
|||
| A magnetic field is a vector field which surrounds magnets and electric currents, and is detected by the force it exerts on moving electric charges and on magnetic materials. <ref> [http://www.rfcafe.com/references/electrical/magnetic-field.htm Magnetic field] </ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math>\overrightarrow{B}</math> |
|||
| <math>T = \frac{W}{M^2}</math> |
|||
| Magnetic (flux density/induction) |
|||
| The amount of magnetic flux in a unit area perpendicular to the direction of magnetic flow <ref> [http://wordnetweb.princeton.edu/perl/webwn?s=magnetic%20flux%20density Magnetic flux density] </ref> |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
[[Image:fieldlines.jpg|thumb|300px|Electric field lines <ref> [http://www.molcad.de/competence/fieldlines.html.en Electric field lines]</ref> ]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
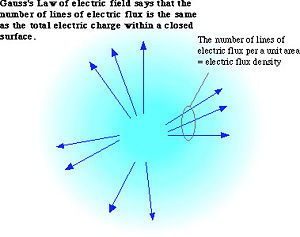
[[Image:Electflux.jpg|thumb|300px|Electric flux density <ref> [http://www.bun.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~suchii/maxwell.eq.html Electric flux density] </ref> ]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{|class="wikitable" border="1" |
|||
! Electric !! Magnetic !! Notes |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math>V = \int \overrightarrow{E} \overrightarrow{dl}</math> |
|||
| <math>\overrightarrow{F} = \int \overrightarrow{H} \overrightarrow{dl}</math> |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math>\sum_{n} V_{n} = 0 = \oint \overrightarrow{E} \overrightarrow{dl}</math> |
|||
| <math>\oint \overrightarrow{H} \overrightarrow{dl} = N i = \sum_{n} H l + N i = 0 </math> |
|||
|Kirchoff's voltage law, Ampere's law |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math>\sum_{n} I_{n} = 0 = \oint_{S} \overrightarrow{J} \overrightarrow{dS}</math> |
|||
| <math>\oint \overrightarrow{B} \overrightarrow{dS} = 0 </math> |
|||
|Kirchoff's current law, The B-field has to go around in a loop |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math>\oint \overrightarrow{J} \overrightarrow{dS} = I</math> |
|||
| <math>\int \overrightarrow{B} \overrightarrow{dS} = \Phi </math> |
|||
|Magnetic flux, Phi |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math> R = \frac{V}{I}</math> |
|||
| <math> \mathfrak{R} = \frac{F}{\Phi} = \frac{N i}{\Phi}</math> |
|||
|Reluctance |
|||
|- |
|||
| <math> I = \frac{V}{R} = G V </math> or <math>\overrightarrow{J} = \sigma \overrightarrow{E}</math> |
|||
| <math>\overrightarrow{B} = \mu H </math> |
|||
| Assumes linearity - exceptions: Hysterisis loop, etc |
|||
|} |
|||
===References=== |
|||
<references/> |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:17, 7 January 2010
Definitions
| Symbol | Units | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flux | A scalar value. The rate of transfer of energy (or another physical quantity) per unit area. <ref> Wiktionary - Flux </ref> | ||
| Electric field (intensity/strength) | The space surrounding an electric charge. It will exert a force on other electrically charged objects. | ||
| Electric (flux density/displacement field) | The amount of electric flux in a unit area perpendicular to the direction of electric field | ||
| Magnetic field (intensity/strength) | A magnetic field is a vector field which surrounds magnets and electric currents, and is detected by the force it exerts on moving electric charges and on magnetic materials. <ref> Magnetic field </ref> | ||
| Magnetic (flux density/induction) | The amount of magnetic flux in a unit area perpendicular to the direction of magnetic flow <ref> Magnetic flux density </ref> |

Electric field lines <ref> Electric field lines</ref>

Electric flux density <ref> Electric flux density </ref>
Analogies between Electric & Magnetic Circuits
| Electric | Magnetic | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Kirchoff's voltage law, Ampere's law | ||
| Kirchoff's current law, The B-field has to go around in a loop | ||
| Magnetic flux, Phi | ||
| Reluctance | ||
| or | Assumes linearity - exceptions: Hysterisis loop, etc |
References
<references/>




















