HW8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
and mathematically as: <math> g(t)= \sum_{-M}^{M}g(\frac{mT}{p})\delta (t-\frac{mT}{p}) </math> and <math> G(f) = \sum_{-M}^{M}g(mT)e^{-j2 \pi mT}</math>. |
and mathematically as: <math> g(t)= \sum_{-M}^{M}g(\frac{mT}{p})\delta (t-\frac{mT}{p}) </math> and <math> G(f) = \sum_{-M}^{M}g(mT)e^{-j2 \pi mT}</math>. |
||
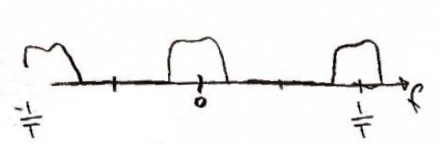
When we run the signal through this filter we multiply it mathematically in the time domain. In the frequency domain this will look like convolution. |
When we run the signal through this filter we multiply it mathematically in the time domain. In the frequency domain this will look like convolution. |
||
[[image:x_frequency4a.jpg]] |
[[image:oversampled.jpg]] [[image:x_frequency4a.jpg]] |
||
x(t)*g(t) and X(f)G(f) |
|||
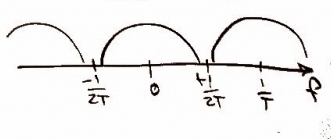
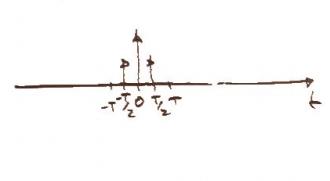
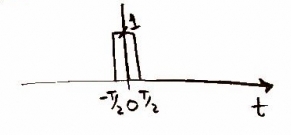
Next we send the signal through a D/A converter. This allows the computer inside the CD player to read the signal information. Graphically this is just a step up and step down a half the period long, known as a pulse function. |
|||
[[image:p_t.jpg]] [[image:p_f.jpg]] |
|||
Lets call these p(t) and P(f). |
|||
Revision as of 01:14, 25 November 2009
Problem Statement
Write a section describing how a CD player works with out oversampling but with digital filtering (1x oversampling)
Solution
CD players are used to play audio files and although these are limited we can look at any non periodic signal as periodic with an infinite period. We can represent this signal, x(t) as such in the time domain and X(f) in the frequency domain.
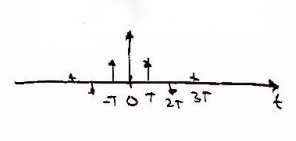
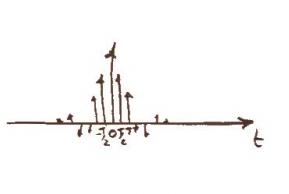
In order to take the signal and read it digitally we must sample it. This gives us data points creating a discrete function of time , where is and integer and is the period between samples. We use a frequency of 44 kHz as it is twice the frequency at which a human can hear (i.e. 2 x 22 kHz) -- that means, kHz. Mathematically sampling is represented by multiplying x(t) with the delta function which results in a convolution with X(f).
Represented as: and respectively.
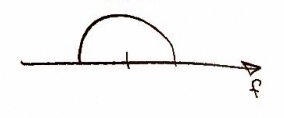
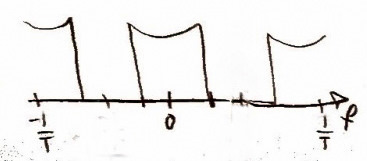
This type of sampling can result in aliasing. This is prevented by oversampling represented on CD players and other media devices as Nx for N times oversampling. It is commonly seen at 8 or 16 and my latest player had it at 52. For this particular assignment we were asked to look at digital filtering but we can accommodate for any oversampling with the variable 'p'. We will use a FIR filter for this. It can be represented graphically as:
and mathematically as: and .
When we run the signal through this filter we multiply it mathematically in the time domain. In the frequency domain this will look like convolution.
x(t)*g(t) and X(f)G(f)
Next we send the signal through a D/A converter. This allows the computer inside the CD player to read the signal information. Graphically this is just a step up and step down a half the period long, known as a pulse function.
Lets call these p(t) and P(f).