Key Facts from Reading: Difference between revisions
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*The output of an ideal differential amplifier is given by <math>\ v_o=A_d v_{id} </math>. |
*The output of an ideal differential amplifier is given by <math>\ v_o=A_d v_{id} </math>. |
||
*The common-mode input signal is given by the following: <math>v_{icm}=\frac{1}{2}(v_{i1}+v_{i2})</math>. |
*The common-mode input signal is given by the following: <math>v_{icm}=\frac{1}{2}(v_{i1}+v_{i2})</math>. |
||
*A real differential amplifier's output is given by <math>\ v_o=A_d v_{id} </math> |
*A real differential amplifier's output is given by <math>\ v_o=A_d v_{id}+A_{cm} v_{icm} </math>, where <math>A_{cm}</math> is the common-mode signal gain. |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Latest revision as of 14:18, 28 January 2010
The following facts are not profound and are possibly very obvious. Nonetheless, they might help cement certain concepts. Please add things you think would be helpful.
Transistors
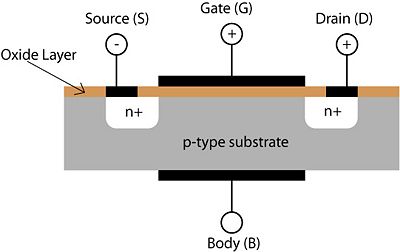
- Conduction in n-type material is from free electrons.
- Conduction in p-type material is from holes (positive particles).
- The function of metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) depends on the voltage applied to the gate.
- Certain ranges of voltage allow no current to flow between the drain and the source. In this way, the MOSFET acts like an open switch.
- Another particular range of voltage allows current to easily flow from the source to the drain.
- When the voltage is in between the ranges of open and closed switch, the MOSFET can smoothly control the amount of current flowing.
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) can act as either switches or current controls as well.
Amplifiers
- An inverting amplifier has a negative voltage gain, Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ {A_{v}}} .
- A noninverting amplifier has a positive voltage gain, Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ {A_{v}}} . (If you get this, you deserve a cookie)
- The power gain,Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ G}
, is the ration of the output power to the input power
- Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G=\frac{P_{o}}{P_{i}}=\frac{V_o{I_o}}{V_o{I_o}}=A_v{A_{i}}=(A_v)^2\frac{R_{i}}{R_{L}}}
- Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ R_i} is the amplifier's input resistance and Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ R_o} is the amplifier's output resistance.
- Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G=\frac{P_{o}}{P_{i}}=\frac{V_o{I_o}}{V_o{I_o}}=A_v{A_{i}}=(A_v)^2\frac{R_{i}}{R_{L}}}
Decibel Conversion
- Power gain, Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ G} , can be converted to decibels:
Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G=(A_v)^2\frac{R_{i}}{R_{L}}}
Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ G_{db}=10 log{A_{v}}^2+10 log R_i - 10 log R_L}
Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ G_{db}=10 log |A_v|+10 log R_i - 10 log R_L}
- By the equation above, we can say voltage gain in decibels can be found with this equation: Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ A_{v dB}=20 log |A_v|} , where Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ A_v} is the voltage gain and Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ A_{v dB}} is the voltage gain is decibels.
- Similarly, we can say current gain in decibels can be found with this equation: Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ A_{i dB}=20 log |A_i|} , where Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ A_i} is the current gain and Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ A_{i dB}} is the current gain is decibels.
Differential Amplifiers
- Differential Amplifiers have two inputs. The terminal marked with a "+" is the noninverting input, and the terminal marked with a "-" is the inverting input.
- The differential input signal is given by Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ v_{id}=v_{i1}-v_{i2} }
- The output of an ideal differential amplifier is given by Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ v_o=A_d v_{id} } .
- The common-mode input signal is given by the following: Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v_{icm}=\frac{1}{2}(v_{i1}+v_{i2})} .
- A real differential amplifier's output is given by Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ v_o=A_d v_{id}+A_{cm} v_{icm} } , where Failed to parse (SVG with PNG fallback (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_{cm}} is the common-mode signal gain.
References
<references/>