Laplace Transform of a Triangle Wave: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michaelvier (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michaelvier (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<math>L\left\{ F\left( t \right) \right\}=\frac{1}{1-e^{-2s}}\left[ \int_{-.5}^{.5}{4te^{-st}dt}+\int_{.5}^{1.5}{-4te^{-st}dt}+\int_{.5}^{1.5}{4.5e^{-st}dt} \right]</math> |
<math>L\left\{ F\left( t \right) \right\}=\frac{1}{1-e^{-2s}}\left[ \int_{-.5}^{.5}{4te^{-st}dt}+\int_{.5}^{1.5}{-4te^{-st}dt}+\int_{.5}^{1.5}{4.5e^{-st}dt} \right]</math> |
||
<math>\int_{}^{}{4te^{-st}}=\; |
<math>\int_{-.5}^{.5}{4te^{-st}}=\; \frac{4e^{.5s}-2se^{.5s}-2se^{-.5s}-4e^{-.5s}}{s^{2}}</math> |
||
<math>\int_{}^{}{-4te^{-st}}=\; L\left\{ -4t \right\}=-\frac{4}{s^{2}}</math> |
<math>\int_{}^{}{-4te^{-st}}=\; L\left\{ -4t \right\}=-\frac{4}{s^{2}}</math> |
||
Revision as of 12:47, 25 January 2010
This page is still in progress
Introduction
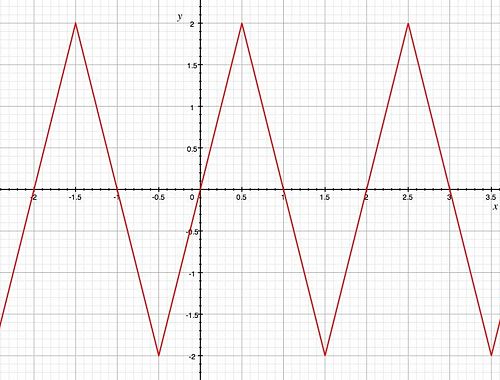
This article explains how to transform a periodic function (in this case a triangle wave). This is especially useful for analyzing circuits which contain triangle wave voltage sources.
Define F(t)
So,
Using the theorem for the transform of a periodic function,


![{\displaystyle L\left\{F\left(t\right)\right\}={\frac {1}{1-e^{-2s}}}\left[\int _{-.5}^{.5}{4te^{-st}dt}+\int _{.5}^{1.5}{\left(-4t+4.5\right)e^{-st}dt}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/13c7a133f6f1a9e0eb1577ae2d4944ca53a1586c)
![{\displaystyle L\left\{F\left(t\right)\right\}={\frac {1}{1-e^{-2s}}}\left[\int _{-.5}^{.5}{4te^{-st}dt}+\int _{.5}^{1.5}{-4te^{-st}dt}+\int _{.5}^{1.5}{4.5e^{-st}dt}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4636da08b8acbe1fa8e686b6ecf5bb78993fe282)


