Laplace transforms: R series with RC parallel circuit: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
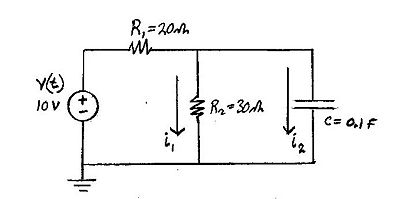
:Find the Voltage across the capacitor for t>=0: |
:Find the Voltage across the capacitor for t>=0: |
||
: |
:Capacitor is uncharged at t(0-) |
||
[[Image:lna_hw_5.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig (1)]] |
[[Image:lna_hw_5.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig (1)]] |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
'''Voltage equations:''' |
|||
Use Loop Equations to solve for the currents in <math>i_1\,</math> and <math>i_2\,</math> |
|||
:equation 1 |
|||
:Loop 1 (Resistor Branch) |
|||
:<math>v(t)=R1(i_1+i_2)+R2(i_1)\,</math> |
:<math>v(t)=R1(i_1+i_2)+R2(i_1)\,</math> |
||
| Line 55: | Line 54: | ||
:equation 2 |
|||
:Loop 2 (Capacitor Branch) |
|||
:<math>v(t)=R1(i_1+i_2)+\dfrac{1}{C}\int{i_2 dt}\,</math> |
:<math>v(t)=R1(i_1+i_2)+\dfrac{1}{C}\int{i_2 dt}\,</math> |
||
| Line 63: | Line 62: | ||
Solve equations (1) and (2) simultaneously |
'''Solve equations (1) and (2) simultaneously''' |
||
| Line 76: | Line 75: | ||
Take the Laplace Transform to move to the S-domain |
'''Take the Laplace Transform to move to the S-domain''' |
||
| Line 95: | Line 94: | ||
Take the inverse Laplace transform to move back into the t-domain |
'''Take the inverse Laplace transform to move back into the t-domain''' |
||
| Line 107: | Line 106: | ||
Voltage on Capacitor |
'''Voltage on Capacitor''' |
||
:<math>v_{capacitor}=10/20(i_1+i_2)\,</math> |
:<math>v_{capacitor}=10/20(i_1+i_2)\,</math> |
||
| Line 126: | Line 125: | ||
===Apply the Initial and Final Value Theorems to find the initial and final values=== |
===Apply the Initial and Final Value Theorems to find the initial and final values=== |
||
:Initial Value Theorem |
:'''Initial Value Theorem''' |
||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sF(s)=f(0)\,</math> |
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sF(s)=f(0)\,</math> |
||
:Final Value Theorem |
:'''Final Value Theorem''' |
||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sF(s)=f(\infty)\,</math> |
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sF(s)=f(\infty)\,</math> |
||
| Line 138: | Line 137: | ||
:Initial Value: |
:'''Initial Value:''' |
||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
||
| Line 148: | Line 147: | ||
:Final Value: |
:'''Final Value:''' |
||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
||
| Line 155: | Line 154: | ||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sV(s)=6\,</math> |
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sV(s)=6\,</math> |
||
:::Final Value = 6 Volts |
:::'''''Final Value = 6 Volts''''' |
||
| Line 162: | Line 161: | ||
:<math>v(t{\infty})=6\,</math> Volts |
:<math>v(t{\infty})=6\,</math> Volts |
||
===Bode Plot=== |
===Bode Plot=== |
||
T-domain |
'''T-domain''' |
||
:<math>V_{in}(t)=10\,</math> |
:<math>V_{in}(t)=10\,</math> |
||
| Line 172: | Line 170: | ||
:<math>V_{out}(t)=6-6*e^-((5/6)t)\,</math> |
:<math>V_{out}(t)=6-6*e^-((5/6)t)\,</math> |
||
S-domain |
'''S-domain''' |
||
:<math>V_{in}(s)=10/s\,</math> |
:<math>V_{in}(s)=10/s\,</math> |
||
| Line 179: | Line 177: | ||
Transfer Function |
'''Transfer Function''' |
||
:<math>H(S)=V(s)_{out}/V(s)_{in}\,</math> |
:<math>H(S)=V(s)_{out}/V(s)_{in}\,</math> |
||
| Line 186: | Line 184: | ||
Bode Plot |
'''Bode Plot''' |
||
| Line 252: | Line 250: | ||
===State Example=== |
===State Example=== |
||
For the voltage on the capacitor... |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<math>\begin{bmatrix} (dv/dt) v_c \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} -200 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} (i_2+i_3) \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} 100 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} V(t) \end{bmatrix}</math> |
|||
Latest revision as of 20:17, 30 November 2009
Problem Statement
- Find the Voltage across the capacitor for t>=0:
- Capacitor is uncharged at t(0-)
Voltage equations:
- equation 1
- ___________________________________equation (1)
- equation 2
- _______________________equation (2)
Solve equations (1) and (2) simultaneously
- Substituting equation (1) into equation (2) gives...
- simplifies to...
Take the Laplace Transform to move to the S-domain
Take the inverse Laplace transform to move back into the t-domain
- substitute this equation back into equation (1)
Voltage on Capacitor
Answer
- Volts
Apply the Initial and Final Value Theorems to find the initial and final values
- Initial Value Theorem
- Final Value Theorem
- Initial Value:
- Initial Value = 0 Volts
- Final Value:
- Final Value = 6 Volts
- Volts
- Volts
Bode Plot
T-domain
S-domain
Transfer Function
Bode Plot
How to use break points and asymptotes to obtain the magnitude frequency response of the system...
The break points are the values of s in H(s) that make the numerator and or the denominator 0.
The location of the break points determines the magnitude frequency response of the system at that frequency.
Zeros are where the numerator is equal to zero.
Poles are when the denominator is equal to zero.
Use Convolution to find the output of the system
State Example
For the voltage on the capacitor...
Written by: Andrew Hellie
Checked by: Kendrick Mensink