Laplace transforms: R series with RC parallel circuit: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
:<math>V(S)=6/s-6(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
:<math>V(S)=6/s-6(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow \infty} sV(s)=0\,</math> |
|||
:Initial Value = 0 Volts |
|||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sV(s)=6s/s-6s(1/(s+(5/6))\,</math> |
|||
::<math>\lim_{s\rightarrow 0} sV(s)=6\,</math> |
|||
:Final Value = 6 Volts |
|||
:<math>v(t0)=0\,</math> Volts |
:<math>v(t0)=0\,</math> Volts |
||
Revision as of 15:26, 22 October 2009
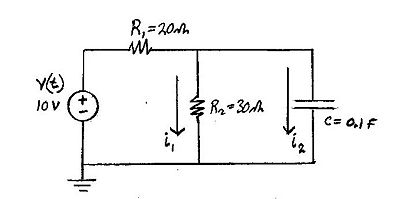
Problem Statement
- Find the Voltage across the capacitor for t>=0:
- Voltage across capacitor at t({0-})=0
Use Loop Equations to solve for the currents in and
- Loop 1
- _______________________________________equation (1)
- Loop 2
- _______________________equation (2)
Solve equations (1) and (2) simultaneously
- Substituting equation (1) into equation (2) gives...
- simplifies to...
Take the Laplace Transform to move to the S-domain
Take the inverse Laplace transform to move back into the t-domain
- substitute this equation back into equation (1)
Voltage on Capacitor
Answer
- Volts
Apply the Initial and Final Value Theorems to find the initial and final values
- Initial Value Theorem
- Final Value Theorem
- Initial Value = 0 Volts
- Final Value = 6 Volts
- Volts
- Volts
Written by: Andrew Hellie
Checked by: