Coupled Oscillator: Hellie: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===Problem Statement=== | ===Problem Statement=== | ||
'''Write up on the Wiki a solution of a coupled oscillator problem like the coupled pendulum. Use State Space methods. Describe the eigenmodes of the system.''' | |||
'''Write up on the Wiki a solution of a coupled oscillator problem like the coupled pendulum. Use State Space methods. Describe the eigenmodes of the system. Solve Using the Matrix Exponential''' | |||
[[Image:Coupled_Oscillator.jpg]] | [[Image:Coupled_Oscillator.jpg]] | ||
| Line 192: | Line 193: | ||
.17764 \\ | .17764 \\ | ||
.94046 | .94046 | ||
\end{bmatrix}, | \end{bmatrix}\, | ||
</math><math>e^{0}\,</math> | </math><math>e^{0}\,</math> | ||
'''Eigenmodes''' | '''Eigenmodes''' | ||
| Line 207: | Line 206: | ||
'''Matrix Exponential using transformation z=Tx''' | |||
<math>T^{-1}=[k_1|k_2|k_3|k_4]\,</math> | |||
<math>z=Tx\,</math> | |||
<math>\dot{z}=TAT^{-1}z \,</math> | |||
<math>\dot{z}=\,</math> | |||
<math>\begin{bmatrix} | |||
-5.2941&0&0&0 \\ | |||
0&2.833i&0&0 \\ | |||
0&0&-2.83333i&0 \\ | |||
0&0&0&5.2941 | |||
\end{bmatrix}\, | |||
</math> | |||
<math>z\,</math> | |||
<math>B=TAT^{-1}=\begin{bmatrix} | |||
-5.2941&0&0&0 \\ | |||
0&2.833i&0&0 \\ | |||
0&0&-2.83333i&0 \\ | |||
0&0&0&5.2941 | |||
\end{bmatrix}\,</math> | |||
''' | |||
<math>z=e^{Bt}z(0)\,</math> | |||
<math>e^{Bt}=\begin{bmatrix} | |||
e^{-5.2941t}&0&0&0 \\ | |||
0&e^{2.833it}&0&0 \\ | |||
0&0&e^{-2.83333it}&0 \\ | |||
0&0&0&e^{5.2941t} | |||
\end{bmatrix}\,</math> | |||
<math>x=T^{-1}z\,</math> | |||
<math>x=T^{-1}e^{Bt}Tx(0)\,</math> | |||
<math>e^{Pt}=T^{-1}e^{Bt}T\,</math> | |||
<math>e^{Pt}=\,</math>lots of variables | |||
'''Another way to solve using the Matrix exponential''' | |||
| Line 228: | Line 276: | ||
<math>[SI-A]^{-1} = \,</math> | <math>[SI-A]^{-1} =\,</math> (something too large for my calculator to display or that I want to type out) | ||
<math>\mathcal{L}^{-1}\left\{[SI-A]^{-1}\right\} = \,</math>(something too large for my calculator to display or that I want to type out) | |||
Written by: Andrew Hellie | Written by: Andrew Hellie | ||
Latest revision as of 22:28, 13 December 2009
Problem Statement
Write up on the Wiki a solution of a coupled oscillator problem like the coupled pendulum. Use State Space methods. Describe the eigenmodes of the system. Solve Using the Matrix Exponential
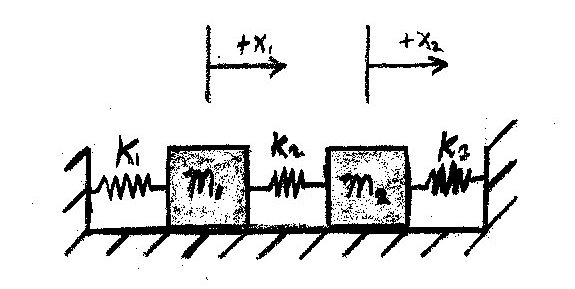
Initial Conditions:
F=ma
State Equations
=
With the numbers...
=
=
Eigenvalues
Eigenvectors
Standard Equation
Eigenmodes
- There are two eigenmodes for the system
- 1) m1 and m2 oscillating together
- 2) m1 and m2 oscillating at exactly a half period difference
Matrix Exponential using transformation z=Tx
lots of variables
Another way to solve using the Matrix exponential
=
(something too large for my calculator to display or that I want to type out)
(something too large for my calculator to display or that I want to type out)
Written by: Andrew Hellie