Chapter 2: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==DC imperfections== |
==DC imperfections== |
||
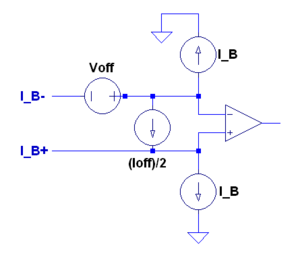
[[Image:DC_Imperfections.PNG |thumb|300px|DC Imperfections]] |
|||
*Bias currents are the average dc currents flowing into the op amp input terminals. They can be caused by the signal source, feedback resistors, etc. |
*Bias currents are the average dc currents flowing into the op amp input terminals. They can be caused by the signal source, feedback resistors, etc. |
||
*The bias current is the average of the dc currents. <math>I_B=\frac{I_{B+}+I_{B-}}{2}</math> |
**The bias current is the average of the dc currents. <math>I_B=\frac{I_{B+}+I_{B-}}{2}</math> |
||
*Offset current is the difference between the bias currents. <math>I_{off} = I_{B+}-I_{B-}\,</math> |
|||
*Offset voltage occurs when the output voltage is nonzero for zero input voltage. |
|||
===Canceling bias currents=== |
|||
*Because bias currents flow have equal magnitude and direction, it is possible to negate their effects. |
|||
**The orientation of the offset voltage and the direction of the offset current are unknown, thus it is not possible to correct for these parameters with a circuit design. |
|||
==Amplifier Circuits== |
==Amplifier Circuits== |
||
Revision as of 15:45, 11 January 2010
Ideal Op Amp Characteristics
- Infinite input impedance
- Infinite open-loop gain for the differential signal
- Zero gain for the common mode signal
- You can easily change an differential amplifier into a common-mode amplifier by grounding one of the inputs
- Zero output impedance
- Infinite bandwidth
- To allow for infinite gain regardless of the frequency? Instantaneous feedback?
Op Amp Nodal Analysis
- No current flows into the + or - terminals
- If negative feedback is present (and no positive feedback), then
- Write nodal equations at and , but not at
- There is a voltage source inside the op amp. Writing a nodal equation at a voltage source adds an extra equation and an extra variable. You gain no ground.
DC imperfections
- Bias currents are the average dc currents flowing into the op amp input terminals. They can be caused by the signal source, feedback resistors, etc.
- The bias current is the average of the dc currents.
- Offset current is the difference between the bias currents.
- Offset voltage occurs when the output voltage is nonzero for zero input voltage.
Canceling bias currents
- Because bias currents flow have equal magnitude and direction, it is possible to negate their effects.
- The orientation of the offset voltage and the direction of the offset current are unknown, thus it is not possible to correct for these parameters with a circuit design.