Magnetic Flux: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=Using Voltage, Time, and Turns of wire= | =Using Voltage, Time, and Turns of wire= | ||
:<math> \Phi_m = V \cdot T / N </math> | :<math> \Phi_m = V \cdot T /over N </math> | ||
where | where | ||
:'''V'''= Voltage | :'''V'''= Voltage | ||
Revision as of 12:32, 30 April 2014
Magnetic Flux
By: Jason Osborne
Reviewed By: Will Griffith & Wesley Brown
Magnetic Flux is the measure of the strength of a magnetic field over a given area. <ref>http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&safe=off&client=firefox-a&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&hs=lBE&defl=en&q=define:magnetic+flux&ei=gsNKS7r4EYuqsgPdmMT_Bg&sa=X&oi=glossary_definition&ct=title&ved=0CAcQkAE</ref>The Greek letter used to represent flux is Φ, phi. The SI unit for magnetic flux is the Weber. The area used must be perpendicular to the
travel of
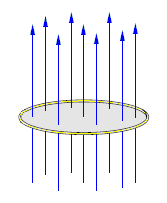
the magnetic lines. The flux can then be determined by how many magnetic lines go
through the area surface. The net flux is the number of magnetic lines going through the area surface in one direction minus the number magnetic lines going through the surface area in the opposite direction. The general quantitative expression for finding magnetic flux is:
where
- B is the magnetic field
- A is the surface area<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_flux</ref>
If specific situations arise and more variables are known the calculations for magnetic flux can become relatively simple. There are many ways to determine magnetic flux from a variety of equations.
Using Voltage, Time, and Turns of wire
where
- V= Voltage
- T= Time
- N= Number of Turns of wire used
Using Magnetomotive force and the Reluctance
where
- F_m= Magnetomotive Force
- R_m= Reluctance
Using Ohm's Law
where
- I= Current
- L= Inductance
- N= Number of Turns of wire used<ref>http://info.ee.surrey.ac.uk/Workshop/advice/coils/terms.html</ref>
Using Area and Magnetic Flux Density
where
- A= Area of surface where density is measured
- B_m=Magnetic Flux Density<ref>Electric Drives an Integrated Approach,Mohan, Ned,2003</ref>
References
<references/>