Aliasing: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
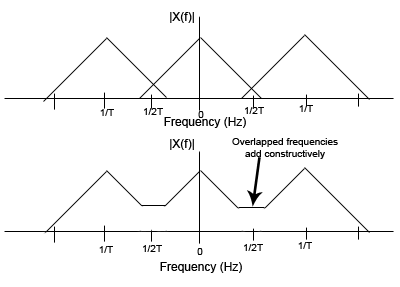
Alaising is what occurs when you sample the highest frequency component of a signal less than two times and then are not able to reconstruct the original signal from the sampled data. This is generalized by Nyquists sampling theorem that says the signal must be sampled at a frequency of 1/T > 2*fmax. | Alaising is what occurs when you sample the highest frequency component of a signal less than two times and then are not able to reconstruct the original signal from the sampled data. This is generalized by Nyquists sampling theorem that says the signal must be sampled at a frequency of 1/T > 2*fmax. | ||
[[Image:alias.gif]] | |||
Revision as of 15:46, 10 December 2004
Alaising is what occurs when you sample the highest frequency component of a signal less than two times and then are not able to reconstruct the original signal from the sampled data. This is generalized by Nyquists sampling theorem that says the signal must be sampled at a frequency of 1/T > 2*fmax.