An Ideal Transformer Example: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
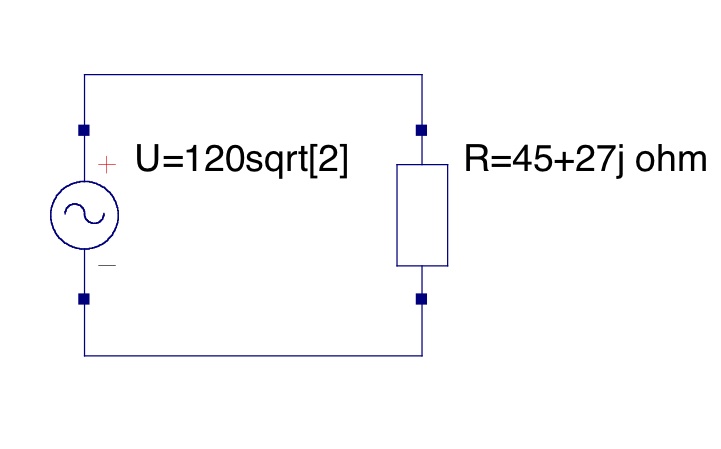
Since this is an ideal transformer, it can be modeled by this simple circuit: | Since this is an ideal transformer, it can be modeled by this simple circuit: | ||
[[Ideal_Circuit.jpg]] | [[Image: Ideal_Circuit.jpg]] | ||
===Contributors=== | ===Contributors=== | ||
Revision as of 23:30, 18 January 2010
Consider a simple, transformer with two windings. Find the current provided by the voltage source.
- Winding 1 has a sinusoidal voltage of ° applied to it at a frequency of 60Hz.
- The combined load on winding 2 is
Solution
, so
Therefore,
Now the Thevenin equivalent impedance, , is found through the following steps:
Now, substituting:
Since ,
Since this is an ideal transformer, it can be modeled by this simple circuit:
Contributors
Read By
John Hawkins