An Ideal Transformer Example: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===Reviwed By=== | ===Reviwed By=== | ||
Andrew Sell - Chris, everything looks fine, though I would do some extra formatting if possible to help make the problem flow a little smoother as you read it, and locate the picture a little higher to help bring the solution together. | Andrew Sell - Chris, everything looks fine, though I would do some extra formatting if possible to help make the problem flow a little smoother as you read it, and locate the picture a little higher to help bring the solution together. | ||
Tyler Anderson - Looks good. | |||
===Read By=== | ===Read By=== | ||
John Hawkins | John Hawkins | ||
Latest revision as of 16:34, 24 January 2010
Consider a simple, transformer with two windings. Find the current provided by the voltage source.
- Winding 1 has a sinusoidal voltage of ° applied to it at a frequency of 60Hz.
- The combined load on winding 2 is
Solution
Given: and
Substituting ,
Therefore,
Now the Thevenin equivalent impedance, , is found through the following steps:
Since this is an ideal transformer and
So we can substitute,
Now, plugging in the given values:
Since this is an ideal transformer, it can be modeled by this simple circuit:
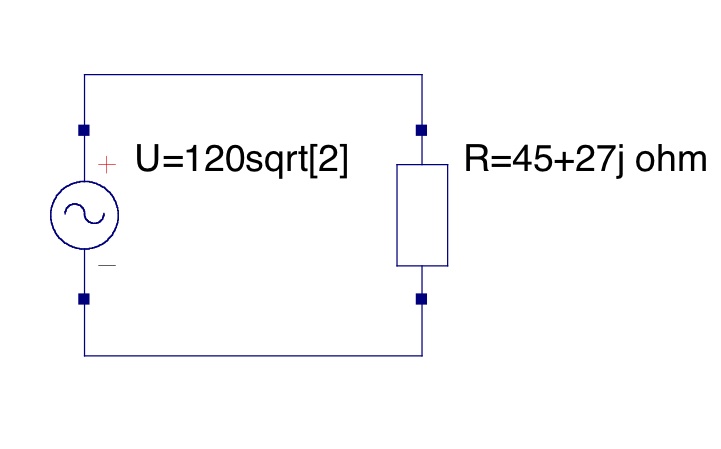
Therefore, ,
Contributors
Reviwed By
Andrew Sell - Chris, everything looks fine, though I would do some extra formatting if possible to help make the problem flow a little smoother as you read it, and locate the picture a little higher to help bring the solution together.
Tyler Anderson - Looks good.
Read By
John Hawkins