Example: Metal Cart: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Amy.crosby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Amy.crosby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Figure 1 will be shown here | Figure 1 will be shown here | ||
[[Emec_cart_polarBear.png]] | [[Image:Emec_cart_polarBear.png]] | ||
[[Emec_cart_polarBear.png|200px|thumb|left|alt text]] to use a 200 pixel wide rendition in a box in the left margin with 'alt text' as description | [[Image:Emec_cart_polarBear.png|200px|thumb|left|alt text]] to use a 200 pixel wide rendition in a box in the left margin with 'alt text' as description | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 25 January 2010
Problem
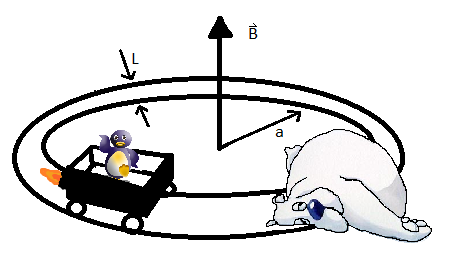
A DC generator is built using a metal cart with metallic wheels that travel around a set of perfectly conducting rails in a large circle. The rails are L m apart and there is a uniform magnetic field normal to the plane as shown in Figure 1. The cart has a mass m and is driven by a rocket engine having a constant thrust F. A wet polar bear lays dead across the tracks acting as if a resistor R is connected as a load. Find The current as a function of time. What is the current after the generator attains the steady-state condition?
Figure 1 will be shown here
to use a 200 pixel wide rendition in a box in the left margin with 'alt text' as description