AM vs FM Modulation: Difference between revisions
New page: ===FM Modulation=== Frequency modulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the carrier wave in response to the amplitude of the modulated signal. A higher-frequency carrier represe... |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
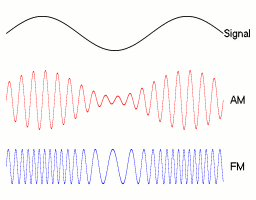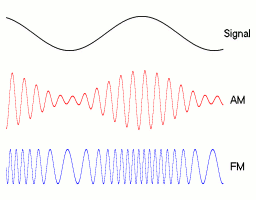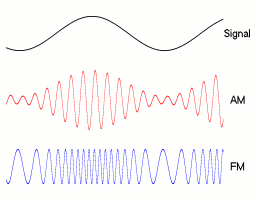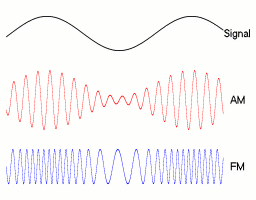
Frequency modulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the carrier wave in response to the amplitude of the modulated signal. A higher-frequency carrier represents larger amplitude, and a lower frequency represents a lower amplitude. This is opposed to AM which changes the amplitude of the carrier wave in response to the modulated signal. | Frequency modulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the carrier wave in response to the amplitude of the modulated signal. A higher-frequency carrier represents larger amplitude, and a lower frequency represents a lower amplitude. This is opposed to AM which changes the amplitude of the carrier wave in response to the modulated signal. | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Amfm3-en-de.gif]] | ||
(image source: wikipedia) | |||
The advantage of FM is a much higher signal integrity over AM because the frequency of a signal doesn't change with distance from source like it does with AM. This means that FM will have the same signal quality right up until its maximum range where the carrier wave is finally overwhelmed by noise and cannot be detected. The disadvantages are a larger bandwidth requirement for the signals since the frequency needs to be able to change within a set range for the modulation to work and the requirement for a more complex receiver since it is more difficult to demodulate than AM. | |||
To demodulate a FM signal, | |||
Revision as of 10:33, 7 April 2010
FM Modulation
Frequency modulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the carrier wave in response to the amplitude of the modulated signal. A higher-frequency carrier represents larger amplitude, and a lower frequency represents a lower amplitude. This is opposed to AM which changes the amplitude of the carrier wave in response to the modulated signal.
The advantage of FM is a much higher signal integrity over AM because the frequency of a signal doesn't change with distance from source like it does with AM. This means that FM will have the same signal quality right up until its maximum range where the carrier wave is finally overwhelmed by noise and cannot be detected. The disadvantages are a larger bandwidth requirement for the signals since the frequency needs to be able to change within a set range for the modulation to work and the requirement for a more complex receiver since it is more difficult to demodulate than AM.
To demodulate a FM signal,